![]()
CBSE Guess > Papers > Important Questions > Class XII > 2013 > Chemistry > P block elements By Mr. R. Srinivas Vasudevamurthy
CBSE CLASS XII
P block elements - 8 Marks Questions
Account for the following:
1. There is a considerable increase in covalent radius from N to P but from As to Bi onlya small change is observed.
2. Ionisation enthalpy of group 15 elements is much higher than that of group 14 elements.
3. Ionic radius of Sb and Bi are very less when compared to the ionic radius of N,P and As.
4. Metallic character of group 15 elements increases on going down the group.
5. Tendency to show – 3 oxidation states in group 15 decreases on going down the group.
6. Nitrogen can’t form penta halides.
7. Nitrogen exhibits pp- pp bonding while heavier members exhibit dp-pp bonding.
8. N2 is a gas while P4 is a solid.
9. Catenation tendency is weaker in nitrogen.
10. N2 molecule is chemically inert while white phosphorus is more reactive.
11. In group 15, +3 oxidation state is more stable than +5 oxidation state on going down the group .
12. R3 P=O is known but R3 N=O is unknown.
13. Basicity of hydrides NH3> PH3 > AsH3 > SbH3 > BiH3
14. Stability of hydrides NH3> PH3 > AsH3 > SbH3 > BiH3
15. Reducing character of hydrides NH3< PH3 < AsH3 < SbH3 <BiH3
16. The oxides in higher oxidation states of group 15 elements are more acidic than that of lower oxidation state.
17. Basicity of group 15 oxides increases on going down the group.
18. PCl5 is more covalent than PCl3.
19. PCl5 is more covalent than PF5.
20. All the five bonds in PCl5 are not equivalent.(Or) PCl5 is more reactive than PCl3.
21. Both PCl3 and PCl5 fumes in air.
22. PH3 has lower boiling point than NH3.
23. NH3 acts as a lewis base.
24. NO2 molecule dimerise to become N2O4.
25. Aluminium is rendered passive in concentrated HNO3.
26. Concentrated HNO3 becomes yellow when exposed to light.(Or) concentrated HNO3 is an oxidizing agent.
27. White phosphorus is more reactive than red phosphorus. Black phosphorus is least reactive.
28. Bond angle in PH4+ is higher than that of PH3.
29. HNH bond angle in NH3 is less than the tetra hedral bond angle of 109.50.
30. Bond angles of HPH,HAsH and HSbH are closer to 900.
31. H3PO4 is tri protic, H3PO3 is diprotic while H3PO2 is mono protic.
32. H3PO2 is a good reducing agent.
33. H3PO2 is a stronger reducing agent than H3PO3.
34. NO is an odd electron molecule but does not dimerise to give N2O2.
35. Sulphur has very high boiling and melting point when compared to oxygen.
36. In group 16 tendencies to show -2 oxidation state decreases on going down the group.
37. In group 16 +4 oxidation state become more stable than +6 oxidation state on going down the group.
38. Oxygen can show a maximum covalency of 4 and it can not form hexa valent compound.
39. Acidity of group 16 hydrides H2O <H2 S < H2Se < H2Te.
40. Reducing character of group 16 hydrides H2O <H2 S < H2Se < H2Te
41. Boiling point of H2O is higher than that of H2 S.
42. Sulphur exhibit +6 oxidation state when it combines with fluorine.
43. SF6 is exceptionally stable or it can not be hydrolysed easily.
44. SF6 is known while SCl6 is unknown.
45. SF6 is known while SH6 is unknown.
46. H2O is a liquid while H2S is a gas.
47. MnO is basic while Mn2O7 is acidic.
48. O3 is thermo dynamically unstable than O2 (or) . O3 in higher concentration is explosive.
49. NO gas depletes ozone layer.
50. Sulphur in vapour state is paramagnetic.
51. HCl and HNO3 are prepared by reacting NaCl and NaNO3 respectively with H2SO4 while HBr and HI can’t be prepared by this method.
52. Cane sugar chars in concentrated sulphuric acid.
53. Concentrated sulphuric acid is a good oxidizing agent.
54. Two S-O bonds in SO2 are equivalent.
55. Ka2 of H2SO4 is << Ka1.
56. Halogens have maximum negative electron gain enthalpy in each period.
57. Fluorine has lesser negative value of electron gain enthalpy than chlorine.
58. All halogens are colored.
59. F2 has smaller enthalpy of dissociation than Cl2.
60. Fluorine has lesser negative value of electron gain enthalpy than chlorine but fluorine is a stronger oxidizing agent than chlorine.
61. Fluorine shows only – 1 oxidation state. Other halogens can exhibit positive oxidation state.
62. Halogens show positive oxidation state when they combine with oxygen and fluorine atoms.
63. Halogens are good oxidizing agent and oxidizing power (reactivity) decreases with the increase in atomic number.
64. Most of reactions of fluorine are exothermic.
65. HF is a liquid while other hydrogen halides are gases.
66. HF has highest boiling point while HCl has lowest boiling point among hydrogen halides.
67. Acidity of hydrogen halides HF<HCl<HBr<HI
68. Thermal stability of hydrogen halides HF>HCl>HBr>HI
69. Thermal stability of group 16 hydrides H2O> H2S> H2Se> H2Te
70. OF2 is fluoride of oxygen and not oxide of fluorine.
71. Oxygen and chlorine has similar electro negativity. Oxygen form hydrogen bonding but not chlorine.
72. Ionic character of halides MF>MCl>MBr>MI
73. Electron gain enthalpy of O → O - is – 141 KJ/mole and O O → O2- is + 702 KJ/mole. Large number of oxides having O2- is known and not O -.
74. In metal halides, halides in higher oxidation state of the metal is more covalent than the one in lower oxidation state.(PbCl4 is more covalent than PbCl2)
75. Inter halogen compound is more reactive than the halogens from which it is formed.
76. Chlorine is a powerful bleaching agent.
77. HCl reacts with Fe to give FeCl2 and not FeCl3
78. Fluorine forms only one oxo acid HOF
79. Acidity of oxo acids HClO4> HClO3> HClO2> HClO.
80. Acidity of oxo acids HOCl>HOBr>HOI
81. Oxidizing power of HClO4> HClO3> HClO2> HClO
82. Fluorine form fluoride of oxygen while other halogens form oxides of halogen.
83. Group 18 elements are chemically unreactive.
84. Group 18 elements have very high ionization enthalpy and it decreases on going down the group.
85. Group 18 elements have positive value of electron gain enthalpy.
86. Group 18 elements have lower value of boiling and melting point and it increases on going down the group.
87. Group 18 elements have larger atomic radius.
88. Bartlett synthesized XePtF6 from his knowledge of earlier known compound O2PtF6.
89. Xenon forms noble gas compounds.
90. Xenon forms compounds only with oxygen and fluorine.
91. Helium is used in diving apparatus.
92. Oxygen has lesser negative value of electron gain enthalpy than Sulphur.
93. XeF, XeF3 and XeF5 not known.
94. Chlorine uses its yellow colour in aqueous solution.
95. CN- is known but CP- is not known.
96. Nitrogen and Bismuth do not form pentavalent compounds.
97. PCl5 solid is ionic in nature.
98. Cr, Al do not dissolve in concentrated HNO3.
99. Both HF and H2O forms Hydrogen bonding but boiling point of H2O is higher than HF
100. Acidic character of PH3<H2S<HCl
101. ONO bond angle in NO2- is higher than that of NO2+
102. N-O bond length in NO2 is shorter than N-O bond length in NO3
103. In HNO3 N-O bond length in NO2 is shorter than N-O bond length in N-OH
104. Oxidising power of Oxoacids of chlorine is HClO4<HClO3<HClO2<HClO
1. Draw the resonating structures of
a) NO
b) NO2
c) N2O
d) N2O3
e) N2O4
f) N2O5 .
g) O3.Also draw the structures of each clearly depicting the bond parameters.
2. Draw the resonance structures of SO2.
3. Draw the structures of
a) NH3
b) HNO3
c) White phosphorus
d) Red phosphorus
e) PCl3
f) PCl5
g) Phosphoric acid
h) Phosphorus acid
i) Hypo phosphorus acid
j) Pyro phosphoric acid
k) cyclic tri meta phosphoric acid
l) Poly meta phosphoric acid.
m) S8
n) S6
o) Sulphuric acid
p) sulphurus acid
q) Peroxo di sulphuric acid
r) Pyro sulphuric acid (oleum)
s) HOCl
t) HClO2
u) HClO3
v) HClO4
w) BrF3
x) IF5
y) IF7
z) IF4-
aa) SF4
bb) SF6
cc) XeOF4
dd) BrO3-
ee) XeF2
ff) XeF4
gg) XeF6
hh) XeOF4
ii) XeO34.Give the formula and structure of noble gas species which is iso structural with
a) ICl4-
b) IBr2-
c) IF6-
d) BrO3-5. Why does nitrogen shows anomalous behavior? Give examples to show the anomalous behavior of nitrogen.
6. Why does oxygen shows anomalous behavior? Give examples to show the anomalous behavior of oxygen.
7. Why does fluorine shows anomalous behavior? Give examples to show the anomalous behavior of fluorine.
8. Describe the method of preparation of
a) NH3 by Haber process
b) HNO3 by Ostwald process
c) H2SO4 by contact process. Give three uses of each.9. Explain brown ring test for nitrate with suitable equations.
10. What is disproportionation reaction? Give equation of the reactions involved in the disproportionation of
a) HNO2
b) Se2Cl2
c) H3PO311. How is ozone estimated quantitatively?
12. Give two uses each of
a) N2
b) PH3
c) O2
d) Ozone
e) SO2
f) Cl2
g) ClO2
h) BrO3
i) I2O5
j) Cl2
k) HCl
l) ClF3
m) He
n) Ne
O) Ar
p) Kr
q) Xe13. How is NH3 (aq) used in salt analysis to determine the presence of
a) Fe3+
b) Zn2+
c) Ag+ in salt analysis.Write the equations of the reactions involved.
14. How is the presence of SO2 detected?
15. What is aqua regia? How does it dissolve noble metals like Au and Pt? Write the equations of the reactions involved.
16. Give differences between white phosphorus and red phosphorus.
17. How is
a) N2
b) O2
c) Cl2 prepared in the laboratory?Write the equations of the reactions involved.
18. How is
a) N2
b) O2
c) Cl2 manufactured in the industry?Write the equations of the reactions involved in the manufacture of Cl2 .
19. How is ammonia prepared in laboratory? Write the equation of the reaction involved.
20. How is HNO3 prepared in laboratory? Write the equation of the reaction involved.
21. How is phosphine prepared from
a) Calcium phosphide
b) White phosphorus. Write the equations of the reactions involved.22. How is PCl5 prepared from
a) Cl2
b) SO2Cl2? Write the equations of the reactions involved23. How is PCl3 prepared from
a) Cl2
b) SOCl2 ? Write the equations of the reactions involved24. How is HCl prepared from NaCl? Write the equations of the reactions involved
25. Write the chemical formula of
a) Chile saltpetre
b) Indian saltpetre
c) Fluorapatite
d) Gypsum salt
e) Epsom salt
f) Baryte
g) Galena
h) Zinc blende
i) Copper pyrite
j) Florospar
k) cryolite
l) Fluoroapatite
m) carnalite.
n) Tear gas
o) mustard gas
p) phosgene26. With what neutral molecule ClO - is iso electronic? Is that molecule a lewis base?
27. Compare the chemistry of a and b Sulphur.What is the transition temperature of a and b Sulphur.
28. How is phosphine purified? Write the equations of the reactions involved.
29. A white waxy solid A on heating in an inert atmosphere forms its allotrope B. A reacts with concentrated alkali to form a toxic gas C. A reacts with excess of chlorine to give D. D on hydrolysis gives an acid E. Identify the compounds. Write the reactions involved.
30. An yellow colored solid A forms its hydride B. B has foul smell and extensively used in salt analysis. B on oxidation gives C. C further gets oxidized in the presence of a catalyst to give D. C decolorize acidified potassium permanganate. Identify the compounds. Write the reaction involved in the conversion of C to D and the reaction of C with acidified potassium permanganate solution.
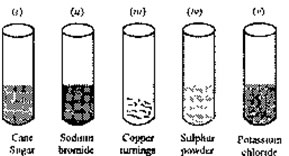
31. Concentrated sulphuric acid is added followed by heating to each of the following test tubes
labelled (i) to (v)
Identify in which of the above test tube the following change will be observed. Support your answer with the help of a chemical equation.
(a) Formation of black substance
(b) Evolution of brown gas
(c) Evolution of colourless gas
(d) Formation of brown substance which on dilution becomes blue
(e) Disappearance of yellow powder along with evolution of colourless gas.32. Give the products and balance the following reactions:
1. HNO2
∆2. NH4Cl +NaNO2
3. (NH4)2Cr2O7
∆4. Ba(N3)2

∆
5. NaN3
∆6. Li + N2
7. Mg +N2
8. N2+H2
Fe 773K
9. N2+O2
200K10. NH2CONH2 +H2O
∆11. NH4Cl +Ca(OH)2
12. (NH4)2SO4+NaOH
13. NH3 +H2O
14. FeCl3+NH4OH
15. ZnSO4+NH4OH
16. Cu2+ NH3
17. AgCl+NH3
18. NaNO3+H2SO4
19. NH3 +O2 Pt/Rh 500K
9 bar20. NO+O2
21. NO2+H2O
22. HNO3+H2O
23. Cu+HNO3 (Dilute)
24. Cu + HNO3 (Conc)
25. Zn+ HNO3 (Dil)
26. Zn+ HNO3 (conc)
27. I2 + HNO3 (conc)
28. C + HNO3 (conc)
29. S8 + HNO3 (conc)
30. P4 + HNO3 (conc)
31. P4+ NaOH+H2O
32. P4 +O2 (Excess)
33. Ca3P2+H2O
34. Ca3P2 +HCl
35. PH3+HI
36. PH3+HBr
37. PH4I +KOH
38. P4 +Cl2
39. P4 + Cl2 (excess)
40. P4+SOCl2
41. P4 + SO2Cl2
42. PCl3 + H2O
43. PCl3 + CH3COOH
44. PCl3 + C2H5OH
45. PCl5 + H2O
46. PCl5 + CH3COOH
47. PCl5 + C2H5OH
48. PCl5 + Ag
49. PCl5 + Sn
50. PCl5
Heat51. H3PO3
Heat52. AgNO3+H2O+H3PO2
53. CuSO4 + PH3
54. HgCl2 + PH3
55. Se2Cl2
Heat
56. KClO3
Heat, MnO2
57. Ag2O
Heat
58. HgO
Heat
59. Pb3O4
Heat60. PbO2
HeatMnO2
61. H2O262. Ca+O2
63. Al + O2
64. C+ O2
65. ZnS+ O2
66. CH4+ O2
67. +O2
68. HCl + O2
69. C2H4+ O2
70. SO2 +H2O
71. CaO+H2O
72. Al2O3+HCl+H2O
73. Al2O3+NaOH+H2O
silent electric discharge
74. O275. PbS +O3
76. I- +H2O + O3
77. I2+Na2S2O3
78. NO+O3
79. SO32- +H+
80. FeS2+O2
81. SO2+H2O
82. SO2+NaOH
83. SO2+Na2SO3+H2O
84. SO2+Cl2
85. SO2+O2
V2O586. SO2+Fe3++H2O
87. SO2+MnO4-+H+
88. SO3+H2SO4
89. H2S2O7+H2O
(X=F,Cl,NO3)
90. MX + H2SO4conc H2SO4
91. C12H22O1192. Cu + conc H2SO4
93. S+ conc H2SO4
94. C+ conc H2SO4
95. F2+2X-
96. Cl2+2X-
97. Br2+2X-
98. F2+H2O
99. X2+H2O
(X=Cl,Br and I)
100. I-+H++O3
101. Mg +Br2
102. MnO2+HCl
103. KMnO4+HCl
104. NaCl+MnO2+HCl
105. Al+ Cl2
106. Fe+ Cl2
107. H2+ Cl2
108. H2S + Cl2
109. C10H16 + Cl2
110. NH3+ Cl2
(excess)111. NH3 + Cl2
(excess)112. NaOH + Cl2
(cold and dilute)113. NaOH + Cl2
(Hot and conc)114. Ca(OH)2 + Cl2
115. CH4+ Cl2
116. C2H4+ Cl2
117. FeSO4+H2SO4+ Cl2
118. Na2SO3+H2O+Cl2
119. SO2+ H2O+Cl2
120. I2 + H2O+Cl2
121. NaCl+H2SO4
122. NaHSO4+NaCl
123. HCl + H2O
124. NH3+HCl
125. Au+H++NO3-+Cl-
126. Pt+ H++NO3-+Cl-
127. Na2CO3+HCl

128. NaHCO3+ HCl
129. Na2SO3+ HCl
130. Fe+ HCl
437K
131. Cl2+F2573K
132. Cl2+F2
(excess)133. I2+Cl2
134. I2+Cl2
(excess)135. Br2+F2
36. Br2+F2

(excess)137. ClF+H2O
138. ClF3+H2O
139. BrF5+H2O
140. IF7+H2O
141. U+ClF3
142. 226
Ra(α decay)
88673K
143. Xe+F21 bar
873K
144. Xe+F2
7 bar
573K
145. Xe+F2
60-70 bar
146. XeF4+O2F2
147. XeF2 +PF5148. XeF4 + SbF5
149. XeF6+MF
(M=Na,K,Rb,Cs)
150. XeF2 +H2O
151. XeF4 +H2O
152. XeF6+H2O
153. XeF6+H2O (partial hydrolysis)
154. XeF6+2H2O (partial hydrolysis)
Submitted By : Mr. R. Srinivas Vasudevamurthy
Email: [email protected]