![]()
CBSE Guess > Papers > Important Questions > Class XII > 2013 > Chemistry > Chemical kinetics (Numerical) By Mr. R. Srinivas Vasudevamurthy
CBSE CLASS XII
Chemical kinetics (Numerical)
1. The decomposition ammonia on a platinum surface follows zero order kinetics.
2NH3(g)N2(g)+3H2(g) K= 2.5x10-4 mole/l/sec. Determine the rate of
a) disapperance of NH3
b) rate of formation of N2
c) rate of formation of H2.2. The decomposition ammonia on a platinum surface follows zero order kinetics.
Calculate the value of rate constant K and the half life of the reaction. GivenTime (seconds) Pressure of NH3(g) in Pascal
0 4x10-2
100 3.5 x10-2
200 3.0 x 10-2
300 2.5 x 10-23. A first order reaction is 20% complete in 10 minutes. Determine the time taken for 80% completion of the reaction.
4. 2A +B
A2B K= 2.5 x10-4 M-2 sec-1 Find the rate when the initial concentrations of [A] = 0.1M [B] = 0.2 M. Also find the rate when 0.04 moles/litre of A has reacted.Rate=K[A][B]2
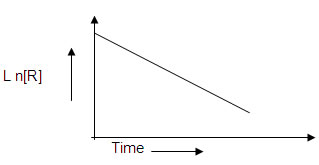
5. For a certain chemical reaction variation in the concentration in [R ] versus time(s) plot is given below
i) what is the order of the reactions?
ii) what are the units of rate constant k?
iii) give the relationship between k and t1/2
iv) what does the slope of the above line indicate?
v) draw the plot [R ] 0 / [R] versus time(s)6. Consider the reaction R → P. The change in the concentration of R with shown in the following plot.

i) Predict the order of the reaction.
ii) Write the expression for half life of this reaction.7. 2NO2+F2
_2NO2F Write the rate of reaction in terms of
(a) rate of formation of NO2F
(b) rate of disappearance of NO2
(c) rate of disappearance of F28. The decomposition of NH3 follows zero order. 2 NH3
N2+3H2 Find the rate of production of N2 and H2.K=2.5x10-4MS-1 −1
9. 2A+B+C_
A2B+C Rate=K(A)(B)2 K=2x10-6M-2S-1Calculate the initial rate when
(A)=0.1M
(B)=0.2M
(C)=0.6M Find the rate when 0.04mole of (A) is consumed.10. 2NO2+F2
_2NO2F
Experiment (NO2)M (F2) M Rate(M/S)
1 0.2 0.05 0.006
2 0.4 0.05 0.012
3. 0.8 0.10 0.048Find the order with respect to NO2 and F2.Also find the overall order of the reaction. Deduce the mechanism of the reaction.
11. Show that(a) 2t½=t¾ (b)Half life of a reaction is 10seconds.Find t2/3
12. Hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution has been studied by titrating liberated acetic acid with NaOH
rate=K(CH3COOCH3) (H2O)
t/min 0 30 60 90
c/M 0.8500 0.8004 0.7538 0.7096Show that it follows pseudo first order reaction as the concentration of water remains constant (1L of water=1000g) What is the value of K?
13. The rates of a reaction starting with initial concentrations 2x10-3−3M and1x10-3M are 2.4x10-4M/s
and0.6x10-4M/s respectively. Find the order of the reaction and rate constant K.
A+5B+6C 3L+3M
Experiment (A)M (B)M (C)M Rate M/minute 1. 0.02 0.02 0.02 00208 2. 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.00104 3. 0.02 0.04 0.02 0.00416 4. 0.02 0.02 0.04 0.00832 Determine the order with respect to each reactant. Find K .Calculate the initial rate when concentration of each reactant is 0.01M.Find the initial rate of change in concentrations of B and L
14. Rate of a reaction becomes 1.414 times when concentration of the reactant is doubled. Find the order of the reaction.
15. (a) show that for a first order reaction t½ is independent of the initial concentration of the reactant.
(b) show that for a zero order reaction t½ is directly proportional to initial concentration of the reactant and inversely proportional to rate constant.
16. Rate constant of a reaction is 2M -1 S -1 at 700K and 32 M -1 S -1 at 800K.Find Ea
17. Rate of a reaction becomes 4 times when temperature changes from 27 0C to 37 0C. Find Ea.
18. Rate constant of a reaction at 700K and 760K are 0.01 M -1 S -1and 0.105 M -1 S -1 respectively. Find A and Ea .
19. Show that for a first order reaction, time required for 99.9% reaction is 10 times the time needed for 50% completion of the reaction.
20. A piece of wood shows C14 activity which is 60% activity found today. Find the age of the sample.t½=5770years.
21. The following data were obtained during the first order decomposition of SO2Cl2 at constant
volume . SO2Cl2(g)SO2(g) +Cl2(g)
Experiment Time(sec) Total pressure(atm)
1 0 0.5
2 100 0.6
Calculate the rate when total pressure is 0.65 atmospheres.22. 2N2O5(g)
2 N2O4(g) +O2(g) follows first order kinetics at constant volume.
Experiment Time(sec) Total pressure(atm)
1 0 0.5
2 100 0.512
Find the value of rate constant K.23. The time required for 10% completion of a first order reaction at 298K is equal to that required for
25% completion at 308K. Find Ea. Calculate K at 318K.24. 2HI(g)
H2(g) +I2(g) Ea at 581K is 209.5KJ/mole. Determine the fraction of molecules
having energy equal to or greater than Ea.25. Ea of a reaction is 75 KJ/mole in the absence of a catalyst and 50KJ/mole in the presence of a Catalyst at 300K. Determine the extent to which the rate of reaction is increased.
26. The rate constant for the first order decomposition of H2O2 is given as logK = 14.34 – 1.25x 104 K/T. Calculate Ea for this reaction. At what temperature will its half life be 256 minutes?
27. The decomposition of hydrocarbon follows the equation K = (4.5x 1011 sec-1) e-28000K/T
Calculate Ea28. 2NO(g) + O2(g)
2NO2(g) occurs in one step. What will happen to the rate when the Volume of the reaction vessel is reduced to 1/3 of the original volume?
29. A reaction is first order with respect to A and second order with respect to B. What will happen to the rate if concentration of A and B are doubled?
30. Rate of a reaction becomes 1.414 times when concentration of the reactant is doubled. Determine the order of the reaction.
31. Rate constant K of a reaction varies with the temperature according to the equation logK = constant- Ea/2.303RT where Ea is activation energy of the reaction. When a plot of logK vs 1/T , a straight line with a slope – 6670K is obtained. Find Ea. [R=8.314J/K/mole]
32. The possible mechanism for the reaction
2 NO(g)+O2(g)
2 NO2(g) is
i) NO(g) +O2(g)
NO3(g) [Fast]
ii) NO3(g) +NO(g)
NO2(g)+NO2(g) [slow]
Submitted By : Mr. R. Srinivas Vasudevamurthy
Email: [email protected]