![]()
CBSE Guess > Papers > Important Questions > Class XII > 2013 > Chemistry > Haloalkanes and Haloarenes By Mr. R. Srinivas Vasudevamurthy
CBSE CLASS XII
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - 4 Marks Questions
1. Give one example each of
a) Markwonikov’s addition.
b) Kharasch effect.
c) Sand Meyer reaction
d) Diazotisation reaction
e) Finkelstein reaction
f) Swarts
g) Wurtz reaction
h) Wurtz Fittig reaction
i) Fittig reaction
j) Friediel's acylation reaction of chloro benzene
k) Friediel craft’s alkylation reaction. of chloro benzene.
l) nitration of chloro benzene.
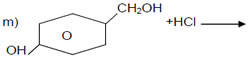
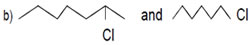
m) sulphonation of chloro benzene.
n) Dehydro halogenation (b elimination reaction)
o) Zatsev rule.
p) chlorination of chloro benzene.2. Explain the classification of halo alkanes based on
a) number of halogen atoms.
b) compounds having sp3 C-X bond
c) compounds having sp2 C-X bond
d) dihalides. Give one example each and their IUPAC names.3. Account for the following:
1) Halo alkanes have higher boiling point than the corresponding parent alkane.
2) Boiling point of halo alkanes RI>RBr>RCl> RF
3) Boiling point of 1-Bromo butane >2-Bromo butane> 1-Bromo- 2-methyl propane> 2-Bromo- 2-methyl propane.
4) Melting point of p-Dichlo benzene is higher than its ortho and meta isomer.
5) Halo alkanes are polar in nature but sparingly soluble in water.
6) Iodo alkane can not be prepared by the reaction of alcohol with KI and sulphuric acid. Phosphoric acid is used in place of sulphuric acid.
7) Order of reactivity of alcohol with HX is tert alcohol> sec alcohol > primary alcohol..
8) Halo arenes can not be prepared by treating phenol with HX or NaX in the presence of sulphuric acid.
9) Iodination of benzene is carried out in the presence of HIO3 or HNO3.
10) Propane on chlorination gives 2-chloro propane as a major product and not 1-chloro propane.
11) Kharasch effect is possible only with HBr and not with HCl and HI.
12) Alcohol reacts with thionyl chloride to give pure halo alkane.
13) Finkelstein reaction of halo alkane is carried out in the presence of dry acetone.
14) Order of reactivity of halo alkanes as per substitution bimolecular nucleophilic is primary halide > secondary halide>tertiary halide.
15) Order of reaction as per substitution unimolecular is tertiary halide>secondary halide >primary halide.
16) Benzylic halides and allylic halides are more reactive towards nucleophile than halo alkanes.
17) Chloro ethene is less reactive towards nucleophile than chloro ethane.
18) Halo arenes are less reactive towards nucleophile than halo alkanes.
19) SN1 mechanism is ruled out in the reaction of halo arenes with nucleophile.
20) Electron with drawing groups like NO2 at ortho and para position with respect to halogen facilitates nucleophillic substitution reaction.
21) Electron with drawing groups like NO2 at meta position with respect to halogen has no effect on nucleophillic substitution reaction.
22) Halo arenes are less reactive towards electrophile than benzene.
23) Although chlorine atom has electron with drawing effect electrophillic substitution occur at ortho and para position.
24) Order of reactivity of alkyl halide RI>RBr>RCl>RF
25) Halo alkanes react with KCN to give alkyl cyanide as a major product while it gives alkyl isocyanide as a major product with AgCN.
26) Halo alkanes give nitrito alkane with KNO2 while nitro alkane with AgNO2.
27) CH3I undergoes SN2 reaction faster than CH3Cl.
4. Explain the following with suitable examples:
a) chiral and chirality
b) enantiomers
c) racemic mixture
d) retention of configuration
e) inversion of configuration.5. Mention the differences between SN1 and SN2 mechanism of halo alkane.
6. Give the products and explain the mechanisms of the following reactions:
a) CH3 CH2 Br + OH-
b) ( CH3)3C-Br + OH-
c) n-BuBr + KOH
7. Carry out the following conversions:
1. Propene to
a) Propan-1-ol
b) Propan-2-ol2. Ethanol to but-1-yne
3. 1-Bromo propane to 2-Bromo propane and vice versa.
4. Toluene to benzyl alcohol.
5. Benzene to
a) 4-bromonitro benzene
b) 3-bromonitro benzene.6. Benzyl alcohol to 2-phenyl ethanoic acid.
7. Ethanol to
a) Propane nitrle
b) Ethyl isocyanide.8. Aniline
a) Chloro benzene
b) Bromo benzene
c) Iodo benzene.9. 2-Chloro butane to 3,4- dimethylhexane.
10. 2-Methyl-1-propene to 2-chloro-2-methylpropane.
11. Ethyl chloride to propanoic acid.
12. But-1-ene to n-butyl iodide.
13. 2-chloropropane to propan-1-ol
14. Isopropyl alcohol to iodoform.
15. Chloro benzene to
a) p-nitro phenol
b) p-chloronitro benzene
c) p-chloro
d) p- chloro acetophenone.
e) p-chloro benzene sulphonic acid
f) 1,4-Dichloro benzene.
g) biphenyl.16. Chloroethane to butane.
17. tert-butyl bromide to isobutyl bromide.
18. Aniline to phenylisocyanide.
19. Propene to
a) 2,3-dimethyl butane
b) n-hexane.20. Tert-butyl bromide to 2-methyl prop-1-ene.
8. What happens when
a) n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH.
b) bromobenzene is treated with Mg in the presence of dry ether.
c) chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis.
d) ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH.
e) methyl bromide is treated with Na in the presence of dry ether.
f) methyl chloride is treated witha) KCN
b) AgCN
c) KNO2
d) AgNO29. Write the structure of the major organic product in each of the following reactions:
acetone
a) CH3CH2Cl + NaI
heatethanol
b) (CH3)3 C-Br +KOH
heatethanol
c) CH3CH2Br + KCN
d) C6H5ONa +CH3Bre) CH3CH2OH +SOCl2
peroxide
f) CH3 CH=CH2 +HBr
g) CH3 CH=CH2 +HBr
h) (CH3)2C=CH2+ HBr
i) CH3CH=C(CH3)2 +HBr
j) CH3CH2CH2OH+SOCl2
k) CH3CH2Br +NaI

+ SOCl2
Heat
+Br2
Br2 Heat
or UV light
+HI
+Mg
A
Dry ether H2O
r) RBr +Mg
A
CH3CH (D)CH3
Dry ether D2O
s) (CH3)3C-C(CH3)3
RX
A
B
Na/ether Mg/ether H2O
10. Arrange the compounds of each set in order of decreasing reactivity towards a) SN2 displacement. b) SN1 displacement.
a) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-bromopentane, 2-bromo pentane
b) 1-bromo-3-methylbutane, 2-bromo-2-methylbutane,3-bromo-2-methylbutane
c) 1-bromo butane, 1-bromo-2-methyl propane, 1-bromo-2-phenyl propane.
d) Methyl chloride, Methyl bromide and Methyl iodide.11. Primary halide A(C4H9Br) with alcoholic KOH gives a compound B. B on treatment with HBr gives C which is an isomer of A. A on treatment with Na in dry ether gives a compound D which is different from when n-butyl bromide is reacted with Na in dry ether. Give the structural formula of A. Write the equations of
the reactions involved.12. An alkyl halide C7H15Br is optically active. It reacts with KOH solution to give racemic mixture. Explain the mechanism of the reaction.
13. Distinguish chemically between
a) CH3Cl, CH3Br, CH3I
b) Chloro benzene and chloro methane
c) chloro benzene and benzyl chloride
d) CHCl3 and CCl414. Primary alkyl halide A (C4H9Br) react with alcoholic KOH to give B.B reacts with HBr to give C which is an isomer of A. When A is treated with sodium in dry ether it gives a compound D C8H18 which is different from the compound when n-butyl bromide is treated with sodium. Give the structural formula of A and complete the reaction.
15. Which alkyl halide from the following pairs would you expect to react more rapidly by SN2 Mechanism? Explain your answer.
a) 1-Bromo butane and 2-Bromo butane.
b) 2-Bromo butane and 2-Bromo-2-methyl propane.
c) Cyclo hexyl chloro methane and chloro cyclo hexane.
d) Iodo butane and chloro butane.16. Which alkyl halide from the following pairs would you expect to react more rapidly by SN1 Mechanism? Explain your answer.

17. Predict the order of reactivity of the following compounds in SN1 and SN2 mechanism.
a) C6H5CH2Br
b) C6H5CH(C6H5) Br
c) C6H5CH(CH3) Br
d) C6H5(CH3)(C6H5) Br. Explain your answer.
18. Arrange the following in the increasing order of boiling point.
a) Bromomethane, Bromoform, Chloromethane and Dibromomethane.
b) 1-Chloropropane, 1-Chlorobutane and isopropyl chloride.19. Among the isomeric alkanes C5H12 , identify the one that on photochemical chlorination yields
a) A single monochloride molecule
b) Three isomeric monochloride molecules
c) Four isomeric monochlorides.
Submitted By : Mr. R. Srinivas Vasudevamurthy
Email: [email protected]