CBSE Guess > Papers > Question Papers > Class X > 2009 > Science > Science
Q. 16. (a) State right hand thumb rule for finding the direction of magnetic
field associated with a current carrying conductor. Draw a labelled
diagram to show the experimental set-up for demonstrating the
rule. Mark the directions of the current and the associated magnetic
field on the diagram.
(b) List two precautions which should be observed for the safety of the user and to avoid short circuiting in domestic circuits. 5
Ans. (a) Right hand thumb rule: See Q.3 (S.A.T.), Chapter 13. [Page 146
Diagram: See Q.14 (S.A.T.), Chapter 13. [Page 148
(b) Precautions which should be observed to avoid short circuiting in
domestic circuits:
(i) Short circuiting can cause fires which can be highly damaging to
electrical appliances and buildings. So, fuse of proper rating must
be used to avoid such damages, as such a fuse-wire will melt
before the temperature of the heated circuit wire gets too high and
the circuit breaks.
(ii) Old wiring should be checked regularly or changed when required.
Or
(a) What is a solenoid? Draw a labelled diagram to show the use of
a current carrying solenoid to magnetise a steel rod. What is the
nature of magnetic field lines inside a solenoid? What do these
lines indicate?
(b) What is an electric fuse? What result do you expect if someone
operates an electric heater of power rating 2 kW, 220 V in a domestic
electric circuit (220 V) that has a fuse of current rating of 5 A? Justify
your answer. 5
Ans. (a) A solenoid is a long coil containing a large number of close turns of
insulated copper wire. The magnetic field produced by a current
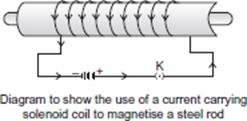
carrying solenoid is similar to the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet. The magnetic field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines. This indicates that the strength of magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid. It is said to be a uniform magnetic field.
(b) An electric fuse is a safety device having a short length of a thin, tinplated copper wire having low melting point, which melts and breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a safe value. • Power of the electric heater,
Power of the electric heater,
P = 2 KW = 2 X 1000 W = 2000 W
Voltage, V = 220 V
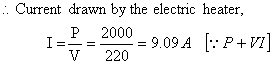
An electric heater withdraws a 9·09 A current but the current rating of the fuse in the circuit is 5 A. Drawing a large quantity of current more than the capacity of fuse makes the fuse burn out. And thus a fuse in the circuit prevents damage to the appliance and the circuit due to overloading.
| Science 2009 Question Papers Class X | |||||||||
| Delhi | Outside Delhi | Compartment Delhi | Outside Delhi | Foreign | |||||
| Set 1 (PDF) | Set 1 (PDF) | Set 1 | Set 1 | Set 1 (PDF) | |||||
| Set 2 | Set 2 | ||||||||
| Set 3 | Set 3 | ||||||||