CBSE Guess > Papers > Question Papers > Class X > 2009 > Science > Science
Q. 8. State Mendeleev’s periodic law. Write two achievements of Mendeleev’s periodic table. 2
Ans. See Q.4 and Q.5 (S.A.T), Chapter 5. [Page 50
Q. 9. Stating two defects in the Mendeleev’s periodic table, explain why it was considered necessary to change the basis of classification of elements from atomic mass to atomic number. 2
Ans. Defects in Mendeleev’s periodic table:
(i) The position of isotopes could not be explained because if the elements are arranged according to atomic mass, the isotopes should be placed in different groups but isotopes were not given separate places in the Mendeleev’s periodic table.
(ii) A correct position could not be assigned to hydrogen in the periodic table as some of its properties resemble those of alkali metals and some of its properties resemble the properties of halogens. The failure of Mendeleev’s periodic law to explain the position of isotopes, wrong order of atomic masses of some elements and position of hydrogen suggested that atomic mass can not be the basis for the classification of elements.
Q. 10. When we immerse a big iron nail in copper sulphate solution taken in a beaker, after about 20 minutes we observe a brownish precipitate on the iron nail and the blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades. What is this type of reaction? State the conclusion you can draw from this observation. 2
Ans. When an iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate solution, then iron sulphate solution and copper metal are formed.

In this reaction, iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution. The deep blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades due to the formation of light green solution of iron sulphate. A reddish brown coating of copper metal is formed on the surface of the iron nail. This is an example of a displacement reaction.
Q. 11. What is a soap? Explain the mechanism of its cleansing action. Why does soap not work well with hard water? 3
Ans.
- A soap is the sodium salt (or potassium salt) of a long chain carboxylic acid (fatty acid) which has cleansing properties in water.
- Cleansing action. See Q.12 (S.A.T.), Chapter 4. [Page 40-41
- Soap does not work well with hard water because hard water contains soluble salts of Ca and Mg. When soap is dissolved in it, insoluble salts of Ca2+ and Mg2+are formed which are called scum. The scum sticks to the clothes being washed and interferes with the cleaning ability of the soap.
Q. 12. What is ethanol? Draw the structure of ethanol molecule. How does
ethanol behave with the following :
(a) Sodium
(b) Excess of conc. sulphuric acid at 443 K
Write chemical equation for each reaction. 3
Ans.
- Ethanol is the second member of the homologous series of alcohol. It’s formula is C2H5OH. It is the most widely used alcohol. It’s common name is ethyl alcohol.
- Structure formula
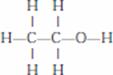
- Ethanol reacts with sodium to form sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas

- When ethanol is heated with excess of conc. sulphuric acid at 443 K, it gets dehydrated to form ethene
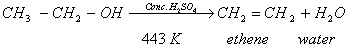
| Science 2009 Question Papers Class X | |||||||||
| Delhi | Outside Delhi | Compartment Delhi | Outside Delhi | Foreign | |||||
| Set 1 (PDF) | Set 1 (PDF) | Set 1 | Set 1 | Set 1 (PDF) | |||||
| Set 2 | Set 2 | ||||||||
| Set 3 | Set 3 | ||||||||