HOMOLOGOUS SERIES
A group of organic compounds having similar structures and similar chemical properties in which the successive compounds differ by CH2 group.
Two adjacent homologous groups differ by 1 carbon atom and 2 hydrogen atoms .
General formula of Alkanes --- CnH2n+2
Characteristics of a Homologus Series
Alkenes ---- CnH2n
Alkynes ---- CnH2n-2
Functional Groups
An ‘atom’ or a ‘group of atoms’ which makes a carbon compound reactive and decides its properties.
Chloro , Bromo and Iodo group ----
When 1 H atom of an alkane is replaced by a halogen atom, we get Haloalkane.
Eg. CH4 → Replace one H by Cl → CH3Cl
General formula is CnC2n+1–X ( X may be Cl ; Br ;I )
Chloromethane – CH3 Cl ---- methyl chloride
Bromomethane - CH3Br ---- methyl bromide
Chloroethane - C2H5Cl ---- ethyl chloride
Chloropropane - C3H7Cl ---- propyl chloride
Alcohol group is made up of 1 oxygen and 1 hydrogen atom joined together.
1 H atom is replaced by an alkane by a hydroxyl group ( OH group)
CH4 → Replace 1 H by OH → CH3OH
General formula is CnH2n+1OH
Methanol - CH3OH ---- methyl alcohol
Ethanol - C2H5OH ---- ethyl alcohol
Propanol - C3H5OH ---- propyl alcohol
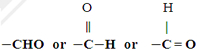
It consists of 1 carbon, 1 hydrogen and 1 oxygen atom joined together.
General formula --- CnH2nO
Methanal - HCHO --- formaldehyde
Ethanal - CH3CHO ---- acetaldehyde
Propanal – CH3CH2CHO --- propionaldehyde
Butanal - CH3CH2CH2CHO
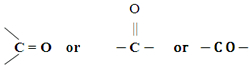
It consists of 1 carbon and 1 oxygen atom. A ketone group must contain at least 3 carbon atoms.
General formula -- CnH2nO
Propanone - CH3COCH3 ---- acetone ( simplest ketone)
Butanone - CH3COCH2CH3
Pentanone - CH3COCH2CH2CH3
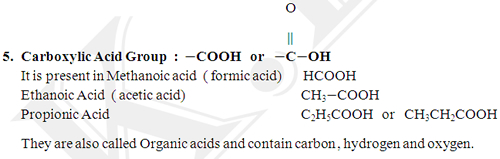
It is a Carbon – carbon double bond.
Ethene - CH2 = CH2
Propene - CH3− CH = CH2
Submitted By Mrs. Kritika Bhola
Email Id : [email protected]