If gross profit is 1/5 if sales given (e.g. 20/100), then Gross profit = 20,
sales = 100 And cost of goods sold = 100–20 = 80 i.e. gross profit is 20/80
of cost. (25% of cost)
OR
If gross profit is 20% of sales then it means 25% on cost
Gross profit is Rs. 20 and sales is Rs. 100 (20/100) = (Cost 100–20 = 80)
gross profit is 20 and cost is 80 (20/80) i.e.
20% of sales = 25% of cost
Illustration 3 : Calculate cost of goods sold and prepares trading account for the year ending 31.03.2011 form the following information :
Opening stock Rs. 30,000; cash sales Rs. 1,60,000; credit sales Rs.
80,000; direct expenses Rs. 5,000; purchases Rs. 1,90,000.
Rate of Gross profit on cost is 33 1 % . Sol. Total sales = cash sales + credit sales= 2,40,000
Let sales Rs. 100 and gross profit 33 1/3
If sales is 2,40,000 then gross profit = 100/3×1/100×2,40,000 = 80,000
Then cost of goods sold = net sales – Gross profit
= 2,40,000–80,000 = Rs. 1,60,000
Calculation of closing stock
Cost of goods sold = opening stock + purchases + direct expense– closing stock
1,60,000=30,000+1,90,000+5000–closing stock
closing stock = 2,25,000–1,60,000 = Rs. 65,000

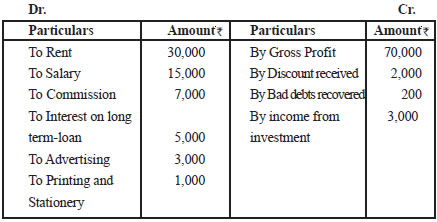
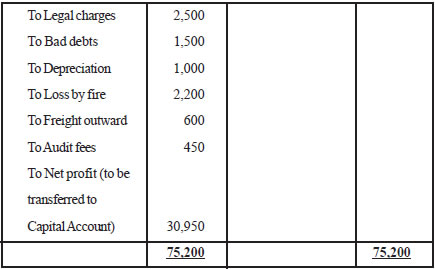
Illustration 4. From the following information, prepare a profit and loss account for the year ending 31st March 2011.
Gross profit Rs. 70,000; Rent Rs. 5,000; Salary Rs. 15,000; Wages Rs. 8,000;
Commission paid Rs. 7,000; Interest paid on long term loan Rs. 5,000; Advertising Rs. 3,000; Discount Received Rs. 2,000; Printing and Stationery Rs. 1,000; Legal Charges Rs. 2,500;
Bad debts Rs. 1,500; Depreciation Rs. 1,000; Income received from investment Rs. 3,000;
Loss by fire Rs. 2,200; Bad debts recovered Rs. 200; freight outward Rs. 600; Audit fees Rs. 450.
Profit and Loss Account
(for the year ended 31st March, 2011)
CBSE Accountancy Class XI ( By Mr. Aniruddh Maheshwari )
Email Id : maheshwari1569@gmail.com