![]()
CBSE Guess > Papers > Important Questions > Class XII > 2012 > Economics > Economics By Mrs. Kritika Bhola
Economics - CBSE CLASS XII
LA (6marks)
Q. 70. Discuss any 6 factors that lead to leftward shift in the demand.
Ans : ecrease in demand leads to leftward shift in the demand curve. The factors that lead to it are :-
1. When income of consumer falls.
2. When price of the substitute good decreases.
3.When price of the complementary good increases.
4.When taste of the consumer shifts against the commodity due to change in fashion or climate.
5.When price of the commodity is expected to increase or decrease in the near future.
6.Decrease in no. of consumers.
Q 71 . Explain with the help of a diagram the effect of the following changes on demand of the commodity:
Ans : 1. A fall in the price of the commodity.
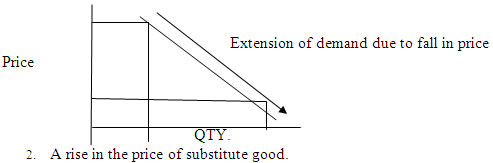
Q 72 . Explain with the help of a diagram the effect of the following changes on demand of the commodity:
1 .An unfavorable change in the taste of the buyer
Ans: Pg. 76 Decrease in demand diag.
2. A fall in the income of the buyer if the good is inferior.
Ans:Pg. 76 Increase in demand diag.
Q 73 Explain the effect of the following on market demand of the commodity:
- Change in the price of related goods
- Change in the number of buyers
- Substitute goods
- Complementary goods
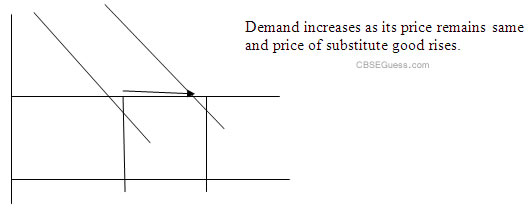
1. When the price of substitute good rises the demand of the commodity increases i.e the demand curve shifts to right and vice versa
2. When the price of complementary good rises the demand of the commodity decreases i.e the demand curve shifts to left and vice versa
Q 74 . Explain the term Change in demand. Represent it graphically and state 3 factors that cause change in demand.
Ans : Change in demand refers to increase or decrease in qty. demanded of a commodity in response to change in other determinants of demand other than price of the same commodity.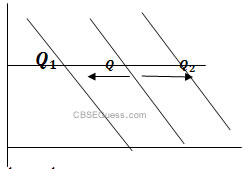
Factors causing change in demand:-
1. Rise or Fall in prices of substitutes.
2. Fall or rise in prices of Complements.
3. Fall or rise in income ( in case of inferior good)Q 75. Define price elasticity of demand. Explain the various degrees of price elasticity of demand using diagrams.
Ans : Price elasticity of demand is a measurement of percentage change in demand due to percentage change in own price of the commodity
Q 76 . Explain how the following determine the price of elasticity:
1) Nature of the commodity
2 ) availability of substitutes
3 ) postponement of the use
Ans : 1. Nature of commodity : Necessaries ( salt, sugar, etc.) and jointly demanded goods ( car and petrol) have inelastic demand as change in prices do not effect their demand. Luxuries have elastic demand.
2. Availability of substitutes : Demand for goods which have substitutes is more elastic because when price of a commodity falls in relation to its substitute its demand rises.
3. Postponement of the use : Demand will be elastic for those commodities whose consumption can be postponed
Q 77 . Prove that elasticity of demand on a downward sloping straight line is given by the ratio of lower segment and upper segment of the demand curve at that point.
Ans : Pg. 99
High Order Thinking Skills questions
Q 78 If the price of the commodity is given as Rs 2 per unit, calculate the optimal level of consumption:
No. of units of X |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
Total Utility |
5 |
9.5 |
13.5 |
17 |
20 |
22.5 |
24.5 |
26 |
MU |
- |
4.5 |
4 |
3.5 |
3 |
2.5 |
4.5 |
6 |
Ans : The optimum level of consumption is at 7 units as till 6 units the MU keeps on decreasing and when he purchases 7 units his MU starts increasing
Q 79 . Give the formula for calculating the slope of the budget line.
Ans : Slope of the budget line = MRE = Qty. of the good sacrificed
Qty. of the good obtained
Q 80 . If the consumer preferences are monotonic, what can you say about the ranking of the following commodity bundles: (10, 10), (10, 9) and (9, 9).
Ans : The utility of the commodity decreases.
Q 81 . What happens to the budget set if both prices as well as income double?
Ans : There is no shift , the BL remains same.
Q 82 . If the price of X rises and demand for commodity Y falls, how are the 2 goods related?
Ans : They are complementary goods.
Q 83 A rise in the income of the consumer leads to fall in the demand of commodity X. What is commodity X called?
Ans : Inferior good.
Q 84 . When demand of a commodity falls to rise in the price of own good, what is it known as?
Ans : Normal good
Q.85 .How does increase in income affect the demand for a) Normal good b) Inferior good?
Ans : Demand of normal good increases and that of inferior good decreases.
Q. 86 When will rise in the demand known as expansion in demand and when will it be known as increase in demand?
Ans : When the demand of good increases due to price only, it is called expansion of demand.
When the demand of good increases due to any other factor except price , it is called
Increase in demand.
Q .87 . Why coefficient of price elasticity of demand is negative?
Ans : It is negative because the price fall leads to rise in qty.
Q . 88 . What will be the elasticity of demand if the demand curve is a horizontal line parallel to x axis?
Ans: Elasticity would be equal to infinity at all the points on the curve because a slight rise in price brings a drastic change and reduces the demand to zero.
Q. 89 . What will be the elasticity of demand if demand curve is vertical line parallel to y axis?
Ans : Elasticity would be equal to zero at all points because there is no effect on demand for the good as the price changes.
Q . 90. What will be the value of elasticity on a rectangular hyperbola demand curve?
Ans: Elasticity would be equal to one because total expenditure would be same at all points.
Q .91 .What is the relationship between slope and elasticity of demand curve?
Ans: Slope is the change in price over change in demand and elasticity is the measurement of change in demand and price in terms of percentage
Q . 92 . The demand for Goods X & Y have equal price elasticity. The demand for X rises from 100 units to 250 units due to 20% fall in is price. Calculate the % rise in demand of Y if its price falls by 8%.
Ans : 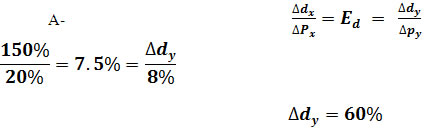
Q . 93. Suppose consumer can afford 6 units of Good 1 & 8 units of Good 2 if he spends his entire income. The price of 2 goods is Rs 6 & Rs 8 respectively. How much is consumer’s income.
Ans: Good 1 Good 2
6 units @ Rs. 6 8 units @ Rs. 8
Rs.36 Rs. 64 = Rs. 100
Q 94 . A consumer wants to consume 2 goods. The prices are Rs 4 & Rs 5 respectively. If the consumers income is Rs 20, answer the following questions-
a) Write down the equation of the budget line.
b) How much of Good 2 can he consume if he spends his entire income on that good
c) What is the slope of Budget line
Ans : a) 4X + 5Y = 20
b ) 20 ÷ 5= 4 units
c ) Slope = 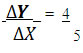
Prepared By: Mrs. kritika bhola
[email protected]
