CBSE Guess > Papers > Question Papers > Class XII > 2006 > Computer Science > Delhi Set - I
Computer science — 2006 (Set I — Delhi)
Q. 1.
- Name the header file to which the following belong
(1)
- abs( )
- isupper( )
- Illustrate the use of #define in C++ to define a macro. (2)
- Rewrite the following program after removing the syntactical error(s), if any. Underline each correction. (2)
# include <iostream.h>
void main()
{ struct STUDENT
{ char stu_name [20];
char stu_sex;
int stu_age=17;
} student;
gets(stu_name);
gets(stu_sex);
} - Find the output of the following program (3)
# include<iostream.h>
#include<string.h>
class state
{ char * state_name;
int size;
public;
state( ); { size=0; state_name=new char[size+1]; }
state(char *s)
{ size = strlen(s) ; state_name = new char[size+1];}
strcpy(state_name,s);
}
void display() {cout<<state name<<endl; }
void Replace (state &a, state &b)
{ size = a.size + b.size;
delete state_name;
state_name = new char[size+1] ;
strcpy(state_name, a.state_name);
strcat(state_name, b.state_name);
}
};
void main( )
{ char *temp = “Delhi”;
state state1(temp), state2(”Mumbai”), state3(”Nagpur”), SI, S2;
SI .Replace(state1, state2);
S2.Replace(S1, state3);
S1.display( );
S2.display( );
} - Find the output of the following program: (2)
#include<iostream.h>
void main( )
{ long NUM = 1234543;
int F = 0, S = 0;
do
{ int Rem = NUM% 10;
if (Rem % 2 !=0)
F+ =R;
else
S+ = R;
NUM/=10;
} while(NUM>0);
cout<<F-S;
} - What are Nested Structures? Give an example. (2)
Q. 2.
- Define Multilevel and Multiple inheritance in context of Object Oriented Programming. Give suitable example to illustrate the same. (2)
- Answer the questions (i) and (ii) after going through the following class:
class Interview
{ int month;
public:
Interview (int y) {month=y ;} //Constructor 1
Interview (Interview&t); //Constructor 2
};- Create an object, such that it invokes Constructor 1 (1)
- Write complete definition for Constructor 2 (1)
- Define a class named ADMISSION in C++ with the following descriptions: (4)
Private members:
AD_NO integer (Ranges 10 - 2000)
NAME Array of characters (String)
CLASS Character
FEES Float
Public Members:- Function Read_Data ( ) to read an object of ADMISSION type
- Function Display() to display the details of an object
- Function Draw-Nos ( ) to choose 2 students randomly.
- Answer the questions (i) to (iii) based on the following code
class stationary
{
char Type;
char Manufacturer [10];
public:
stationary();
void Read_sta_details( );
void Disp_sta_details( );
};
class office: public stationary
{
int no_of_types;
float cost_of_sta;
public:
void Read_off_details( );
void Disp_off_details( );
};
class printer: private office
{
int no_of_users;
char delivery_date[10];
public:
void Read_pri_details( );
void Disp_pri_details( );
};
void main ( )
{ printer MyPrinter; }
- Mention the member names which are accessible by MyPrinter declared in main() function (1)
- What is the size of MyPrinter in bytes? (1)
- Mention the names of functions accessible from the member function
Read_pri_details () of class printer. (2)
Q. 3.
- Write a function in C++ which accepts an integer array and its size as arguments/parameters and assign the elements into a two dimensional array of integers in the following format. 3
����������������������If the array is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
The resultant 2 D array is given belowIf the array is 1, 2, 3
The resultant 2 D array is given below1
1
1
1
1
12
2
2
2
2
03
3
3
3
0
04
4
4
0
0
05
5
0
0
0
06
0
0
0
0
01
1
12
2
03
0
0 - An array MATI3OII1OJ is stored in the memory column wise with each element occupying 8 bytes of memory. Find out the base address and the address of element MATI2OII5I, if the location of MATI5JL7] is stored at the address 1000. (4)
- class queue (4)
{ int data [10];
int front, rear;
public:
queue ( ) (front= -1; rear= -1;)
void add( ); //to add an element into the queue
void remove( ); //to remove an element from the queue
void Delete(int ITEM); //To delete all elements which are equal to ITEM
} ;
Complete the class with all function definitions for a circular array Queue. Use another queue to transfer data temporarily - Write a function in C++ to perform Push operation on a dynamically allocated stack containing real number. (3)
- Write the equivalent infix expression for
a, b, AND, a, c, AND, OR (2)
Q. 4.
- void main( ) (1)
{ char=’A’;
fstream fileout(”data.dat”,ios::out);
fileout<<ch;
int p = fileout.tellg( );
cout<<p;
}
What is the output if the file content before the execution of the program is the string “ABC” (Note that” “are not part of the file) - Write a function to count the number of words present in a text file named “PARA.TXT”. Assume that each word is separated by a single blank/space character and no blanks/spaces in the beginning and end of the file. (2)
- Following is the structure of each record in a data file named “COLONY.DAT”. (3)
struct COLONY
{ char Colony Code[10];
char Colony Name[10];
int No of People;
};
Write a function in C++ to update the file with a new value of No _of_People. The value of Colony_Code and No_of_People are read during the execution of the program.
Q. 5.
- What is an Alternate Key? (2)
- Study the following tables DOCTOR and SALARY and write SQL commands for the questions (i) to (iv) and give outputs for SQL queries (v) to (vi): (6)
TABLE : DOCTOR
ID |
NAME | DEPT | SEX |
EXPERIENCE |
101 |
John | ENT | M |
12 |
104 |
Smith | ORTHOPEDIC | M |
5 |
107 |
George | CARDIOLOGY | M |
10 |
114 |
Lara | SKIN | F |
3 |
109 |
K George | MEDICINE | F |
9 |
105 |
Johnson | ORTHOPEDIC | M |
10 |
117 |
Lucy | ENT | F |
3 |
111 |
Bill | MEDICINE | F |
12 |
130 |
Morphy | ORTHOPEDIC | M |
15 |
TABLE : SALARY
1D |
BASIC |
ALLOWANCE |
CONSULTATION |
101 |
12000 |
1000 |
300 |
104 |
23000 |
2300 |
500 |
107 |
32000 |
4000 |
500 |
114 |
12000 |
5200 |
100 |
109 |
42000 |
1700 |
200 |
105 |
18900 |
1690 |
300 |
130 |
21700 |
2600 |
300 |
- Display NAME of all doctors who are in “MEDICINE” having mo than 10 years experience from the table DOCTOR.
- Display the average salary of all doctors working in “ENT” department using the tables DOCTOR and SALARY. Salary = BASIC + ALLOWANCE
- Display the minimum ALLOWANCE of female doctors.
- Display the highest consultation fee among all male doctors.
- SELECT count( * ) from DOCTOR where SEX “F”
- SELECT NAME, DEPT, BASIC from DOCTOR, SALARY where DEPT = “ENT” and DOCTOR.ID = SALARY.ID
Q. 6.
- State and verify Distributive Law. (2)
- Write the equivalent expression for the following Logical Circuit: (2)
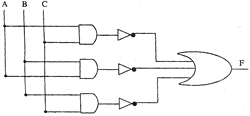
- Express P+Q’R in canonical SOP form. (1)
- Reduce the following Boolean expression using K-Map. (3)
F(P, Q ,R, S) = ∑ (0,3,5,6,7,11,12,15)
Q. 7.
- Differentiate between Internet and Intranet. (1)
- Expand the following terms
- CDMA
- URL
- HTTP
- WAN (2)
- Write one advantage of STAR topology as compared to BUS topology. (1)
- UNIVERSITY OF CORRESPONDENCE in Allahabad is setting up the network between its different wings. There are 4 wings named as Science (S), Journal ism (J), ARTS (A) and Home Science (H).
Distance between various wings are given below
| Wing A to Wing S | 100 m |
| Wing A to Wing J | 200 m |
| Wing A to Wing H | 400 m |
| Wing S to Wing J | 300m |
| Wing S to Wing H | 100m |
| Wing J t o Wing H | 450m |
Number of Computers
| Wing A | 150 |
| Wing S | 10 |
| Wing J | 5 |
| Wing H | 50 |
- Suggest a suitable Topology for networking the computer of all wings. (1)
- Name the wing where the Server to be installed. Justify your answer. (1)
- Suggest the placement of Hub/Switch in the network. (1)
- Mention an economic technology to provide Internet accessibility to all wings. (1)
| Computer Science 2006 Question Papers Class XII | |||||||
| Delhi | Outside Delhi | Compartment Delhi | |||||
| Set I | Set I | Set I | |||||
