Why did Fayol suggest the idea of ‘GANG PLANK’? What light does it throw on the nature of Fayol’s principles? – 5 marks
Or
Illustrate SCALAR CHAIN with suitable example? 3 marks – V. Important
Fayol's Scalar Chain
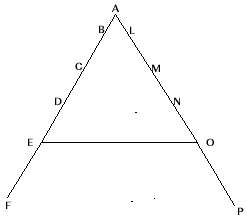
What is GANG-PLANK? Show it through a diagram – 3 marks
Gang-plank is the technique of shortening the route of communication which is usually followed through all channel of hierarchy. Fayol suggested that in case of urgencies, by jumping the prescribed line of authority, these officials could deal with one another at one sitting and sort out several problems quickly.
How can Fayol’s PRINCIPLES OF EQUITY and order be applied in work situation?-4 marks. Illustrate with an example. (CBSE-1996, CBSE-2001)
Or
Which principle of management aims at securing the loyalty and devotion of the employees by giving them kind, fair and just treatment? Explain this principle with a suitable example -4 marks
Name the function of management, which concentrates on employing and retaining the right person at the right place. Explain why this function is important in any organisation.
Or
If an organisation does not provide the right place for physical and human resources in the organisation., which principle is violated? What are the consequences of it?
Principle of ORDER:
If an organisation does not provide the right place for physical and human resources in the organisation, the PRINCIPLE OF ORDER is violated.
The principle of order is concerned with proper arrangement of things and people. This principle can be divided into two:
Material order: An orderly arrangement of things is called material order. There should be an orderly arrangement of physical factors of production like land, raw material, tools and equipment. This means that there should be a specific place for everything. Every piece of land and every article should be used properly, economically and in the best possible way.
Social order: An orderly arrangement of people is called social order. This includes employees. Right man for the right job will ensure effective use of man power resources. Right place for everything and for everyone should therefore be the guiding principle for every management.
Adverse Effect: When there is no arrangement for things and people, the organisation will not be able to achieve its objectives in time. Effective utilisation of physical and human resources will not be possible.
Explain the principle of “INITIATIVE” through a suitable example - 3 marks (CBSE-2000)